Preparing the data for surface loads (case 1)¶
Load main libraries, set paths and adjust plotting theme (optional)
[1]:
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
pv.set_jupyter_backend('static')
pv.global_theme.background = 'white'
pv.global_theme.color = "beige"
pv.global_theme.show_edges = True
pv.global_theme.window_size = [800, 400]
STATICS_DIR = Path("../../../../_static")
HEXBEAM_MULTIBLOCK_FILEPATH = STATICS_DIR / "hexbeam_multiblock_surface_load_case_1.vtm"
Load the Mesh¶
In this examples, we are simply interested in manipulating the FEB file and not the mesh itself, therefore we will be used pre-defined mesh. If you wish to create the mesh using python, we recommend using the pyvista or the gmsh and pygmsh libraries.
[2]:
mb = pv.read(HEXBEAM_MULTIBLOCK_FILEPATH)
mb
[2]:
| Information | Blocks | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Extract each block from the multiblock
[3]:
grid = mb["grid"]
selected_load_surface = mb["selected_load_surface"]
Extract the field data (just to make it easier later on)
[4]:
grid_boundary_ids = grid.field_data["boundary_ids"]
load_surface_connectivity = selected_load_surface.field_data["load_surface_connectivity"]
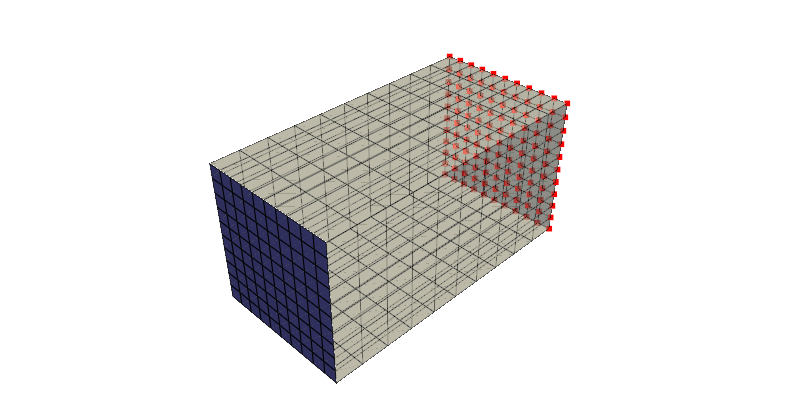
Plot data
[5]:
plotter = pv.Plotter()
plotter.add_mesh(grid, color="beige", opacity=0.5)
plotter.add_points(grid.points[grid_boundary_ids], color="red", point_size=6)
plotter.add_mesh(selected_load_surface, color="blue", point_size=6)
plotter.show()
Create FEB¶
Create a FEB object:¶
[6]:
from febio_python import Feb
feb = Feb(version=3.0)
Setup basic configurations:¶
[7]:
feb.setup_module(module_type="solid") # default values
feb.setup_globals(T=0, R=0, Fc=0) # default values
feb.setup_controls(analysis="static") # here, you can change basic settings. See docs for more info.
feb.setup_output(variables=["displacement", "Lagrange strain", "stress"]) # default values
Add materials¶
[8]:
from febio_python.core import Material
# Define the material
material_1 = Material(
id=1,
type="isotropic elastic",
name="FirstBlockMaterial",
parameters=dict(
E=2e3,
v=0.3,
density=1,
)
)
Add the material to the FEB object
[9]:
feb.add_materials([material_1])
Add mesh¶
[10]:
from febio_python.core import Nodes, Elements
# Define the nodes
grid_nodes = Nodes(name="FirstBlockNodes", coordinates=grid.points)
# Define the elements
grid_elements = Elements(
name="FirstBlockElements",
type="HEXAHEDRON",
connectivity=grid.cells_dict[pv.CellType.HEXAHEDRON],
mat=1
)
Add the nodes and elements to the FEB object
[11]:
feb.add_nodes([grid_nodes])
feb.add_elements([grid_elements])
Add mesh domains¶
[12]:
from febio_python.core import SolidDomain
# create a solid domain
solid = SolidDomain(
id=1,
name="FirstBlockElements", # this must match one of the element names
mat="FirstBlockMaterial", # this must match one of the material names
)
Add domains to the FEB object
[13]:
feb.add_mesh_domains([solid])
Add Nodesets¶
[14]:
from febio_python.core import NodeSet
# Define the node sets
boundary_nodeset = NodeSet(
name="BoundaryNodes",
ids=grid_boundary_ids
)
Add node sets to the FEB object
[15]:
feb.add_node_sets([boundary_nodeset])
Add Boundary conditions¶
[16]:
from febio_python.core import FixCondition
# create the fixed boundary condition
fixed = FixCondition(
dof="x,y,z", # fix only the z direction
node_set="BoundaryNodes",
name="Fixed")
Add the fixed boundary condition to the FEB object
[17]:
feb.add_boundary_conditions([fixed])
Add Surfaces¶
[18]:
from febio_python.core import Surfaces
# Define the surface
surface = Surfaces(
name="LoadSurface",
type="QUAD",
connectivity=load_surface_connectivity,
)
Add surface to the FEB object
[19]:
feb.add_surfaces([surface])
Add loads¶
[20]:
from febio_python.core import SurfaceLoad, LoadCurve
# Define the surface load
load = SurfaceLoad(
surface="LoadSurface", # this is the surface name (must be in the FEB object)
load_curve=1, # this is the load curve ID
name="SurfaceLoad", # optional name
scale=-1000, # scale factor
linear=True, # linear pressure load
symmetric_stiffness=True) # symmetric stiffness matrix
# Define the load curve
lc = LoadCurve(
id=1,
interpolate_type="linear",
data=np.array([[0, 0], [1, 1]]))
Add load and load curve to the FEB object
[21]:
feb.add_surface_loads([load])
feb.add_load_curves([lc])
Writing FEB¶
[22]:
output_file = STATICS_DIR / "sample_surface_load_case_1_v30.feb"
feb.write(output_file)